Singularity
Introduction to Singularity
- Focus:
Reproducibility to scientific computing and the high-performance computing (HPC) world.
Origin: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Later spin-off: Sylabs
Version 1.0 -> 2016
More information: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Singularity_(software)
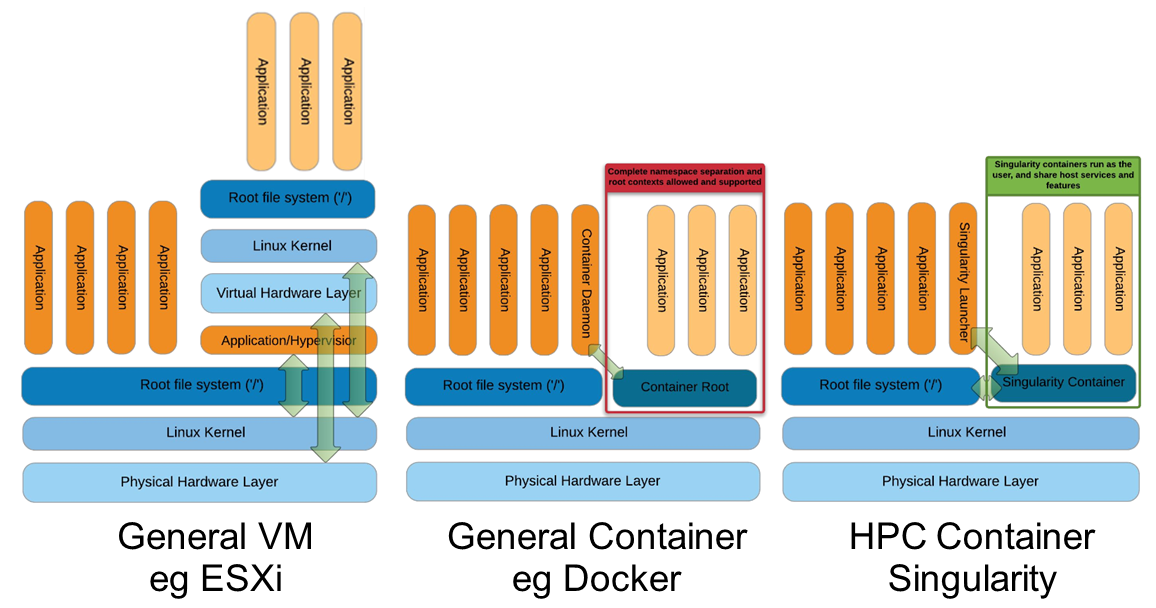
Singularity architecture
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
|---|---|
No dependency on a daemon |
At the time of writing, only good support in Linux |
It can be run as a simple user |
Mac experimental. Desktop edition. Only running |
It avoids permission headaches and hacks |
For some features, you need a root account (or sudo) |
Image/container is a file (or directory) |
|
More easily portable |
|
Two types of images: Read-only (production) |
|
Writable (development, via sandbox) |
Trivia
Nowadays, there may be some confusion since there are two projects:
They “forked” in 2021. So far, they share most of the codebase, but eventually, this could be different, and the software might have different functionality.
The former is already “End Of Life,” but its development continues under the name Apptainer http://apptainer.org/>`_, with the support of the Linux Foundation.
Container registries
Container images, typically different versions, are stored in container repositories.
These repositories can be browsed or discovered within normally public container registries.
Docker Hub
It is the first and most popular public container registry (which also provides private repositories).
Example:
https://hub.docker.com/r/biocontainers/fastqc
singularity build fastqc-0.11.9_cv7.sif docker://biocontainers/fastqc:v0.11.9_cv7
Biocontainers
Website gathering bioinformatics-focused container images from different registries.
Originally, Docker Hub was used, but now other registries are preferred.
Example: https://biocontainers.pro/tools/fastqc
Via quay.io
https://quay.io/repository/biocontainers/fastqc
singularity build fastqc-0.11.9.sif docker://quay.io/biocontainers/fastqc:0.11.9--0
Via Galaxy project prebuilt images
singularity pull --name fastqc-0.11.9.sif https://depot.galaxyproject.org/singularity/fastqc:0.11.9--0
The Galaxy project provides all Bioinformatics software from the BioContainers initiative as Singularity prebuilt images. If image download and conversion time is an issue, this might be the best option for those working in the biomedical field.
Running and executing containers
We can run processes once we have some image files (or directories) ready.
Singularity shell
The straightforward exploratory approach is equivalent to docker run -ti biocontainers/fastqc:v0.11.9_cv7 /bin/shell but with a more handy syntax.
singularity shell fastqc-0.11.9.sif
Move around the directories and notice how the isolation approach differs from Docker. You can access most of the host filesystem.
Singularity exec
This is the most common way to execute Singularity (equivalent to docker exec), and it would be the normal approach in an HPC environment.
singularity exec fastqc-0.11.9.sif fastqc
Test a processing of a file from Git data directory:
singularity exec fastqc-0.11.9_cv7.sif fastqc B7_input_s_chr19.fastq.gz
Environment control
By default, Singularity inherits a profile environment (e.g., PATH environment variable). This may be convenient in some circumstances, but it can also lead to unexpected problems when your environment clashes with the default one from the image.
singularity shell -e fastqc-0.11.9.sif
singularity exec -e fastqc-0.11.9.sif fastqc
Compare env command with and without -e modifier.
singularity exec fastqc-0.11.9.sif env
singularity exec -e fastqc-0.11.9.sif env
Singularity advanced aspects
Bind paths (aka volumes)
Paths of the host system mounted in the container.
Default ones, no need to mount them explicitly (for 3.6.x):
`$HOME`,`/sys:/sys`,`/proc:/proc`,`/tmp:/tmp`,`/var/tmp:/var/tmp`,`/etc/resolv.conf:/etc/resolv.conf`,`/etc/passwd:/etc/passwd`, and`$PWD`Ref
For others, need to be done explicitly (syntax: host:container)
mkdir test
touch test/testout
singularity shell -e -B ./test:/scratch fastqc-0.11.9.sif
> touch /scratch/testin
> exit
ls -l testdir
Exercise
Using the 2 fastq available files, process them outside and inside a mounted directory using fastqc.
Suggested solution
# Let's create a dummy directory
mkdir test
# Let's copy the contents of the data directory in that directory
singularity exec fastqc.sif fastqc test/*fastq.gz
# Check you have some HTMLs there. Remove them
rm test/*html
# Let's use shell
singularity shell fastqc.sif
> cd test
> fastqc *fastq.gz
> exit
# Check you have some HTMLs there. Remove them
singularity exec -B ./test:/scratch fastqc.sif fastqc /scratch/*fastq.gz
# What happens here!
singularity exec -B ./test:/scratch fastqc.sif bash -c 'fastqc /scratch/*fastq.gz'
Singularity tips
Troubleshooting
singularity --help
Singularity cache directory
$HOME/.singularity
It stores cached images from registries, instances, etc.
If problems may be a good place to clean. When running
sudo, $HOME is /root.
Global singularity configuration
Normally at /etc/singularity/singularity.conf or similar (e.g., preceded by /usr/local/)
It can only be modified by users with administration permissions
Worth noting
bind pathlines, which point default mounted directories in containers