Introduction: What is RNA-Seq?
| RNA molecule |
|---|
 |
| from Wikipedia |
Types of RNAs
In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are 3 main types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA, aka mRNA:
- Represent ~1-5% of total RNA mass;
- Protein-coding;
- Mostly poly-adenylated (at the 3’);
- Very heterogeneous in terms of base sequence and size.
- Ribosomal RNA, aka rRNA:
- Represent ~80-90% of total RNA.
- Transfer RNA, aka tRNA:
- Represent ~15% of total RNA
- Small in size: ~ 75-95 nt
But there are many more types of RNAs:
- Micro RNA, aka miRNA:
- Regulatory RNAs;
- Small in size: ~20-25 nt.
- Small nuclear RNA, aka snRNA:
- Some of snRNA are related to splicing mechanisms.
- And many more: lncRNA, eRNA, scaRNA, gRNA, piRNA, etc.
| Estimate of RNA levels in a typical mammalian cell |
|---|
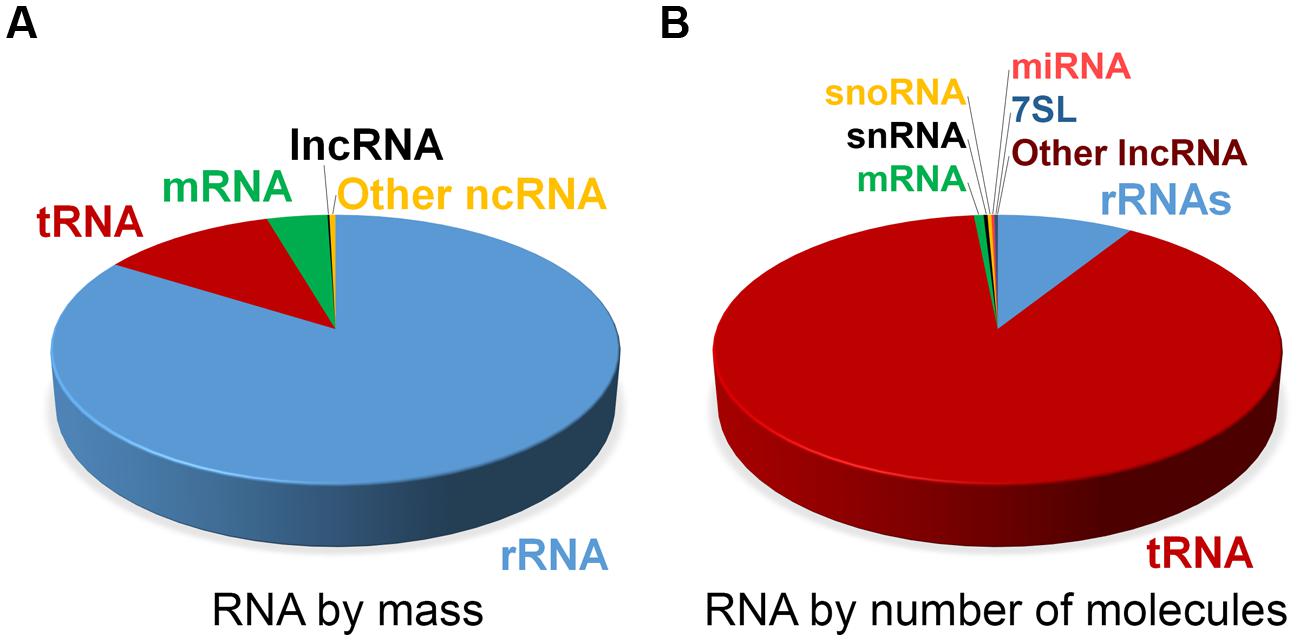 |
| from Palazzo and Lee, Frontiers in Genetics, 2015 |
RNA-sequencing
RNA-sequencing, aka RNA-seq, is a High-Throughput Sequencing technique for identifying and quantifying RNA molecules in biological samples.
| RNA-Seq summary |
|---|
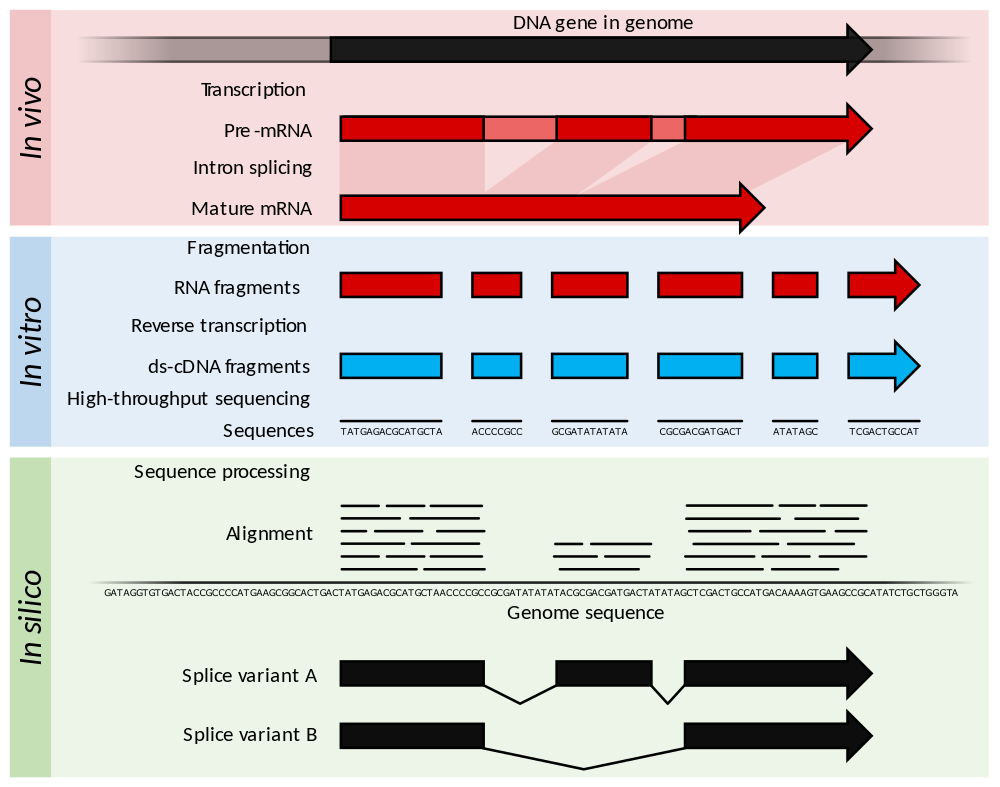 |
| from Wikipedia |
This technology is used to analyze RNA for assessing:
- RNA/gene/transcript expression;
- alternatively spliced transcripts;
- gene fusion and SNPs;
- post-translational modification.
Other technologies for assessing RNA expression are Northern Blot, real-time PCR, hybridization-based microarrays.
Technologies and protocols
RNA-seq can target different RNA populations, using different protocols:
- Positive selection of mRNAs: polyA selection.
- Negative selection of non-polyA: rRNA depletion.
- Size selection: e.g. small RNA selection.
Depending on the technology and the protocol, RNA-seq can produce:
- Single-end short reads (50-450 nt), which are used for gene expression quantification (mainly Illumina, but also Ion Torrent and BGISEQ);
- Paired-end reads (2 x 50-250 nt), which are useful for detecting splicing events and refinement of transcriptome annotation;
- Single long reads (PACBio or ONT), which are used for the de novo identification of new transcripts and improving transcriptome assembly.

