Part14 Conditional statement
Conditional statements are expressions that perform different computations or actions depending on whether a predefined boolean condition is TRUE or FALSE.
“if” statement
Structure of the if statement:
If the condition is TRUE, then proceed to the action_command; if it is FALSE, then nothing happens.
Note the usage of curly brakets {} to start and end the conditional!
With else
If the condition is TRUE, then proceed to action_command1; if the condition is FALSE, proceed to action_command2.
With else if
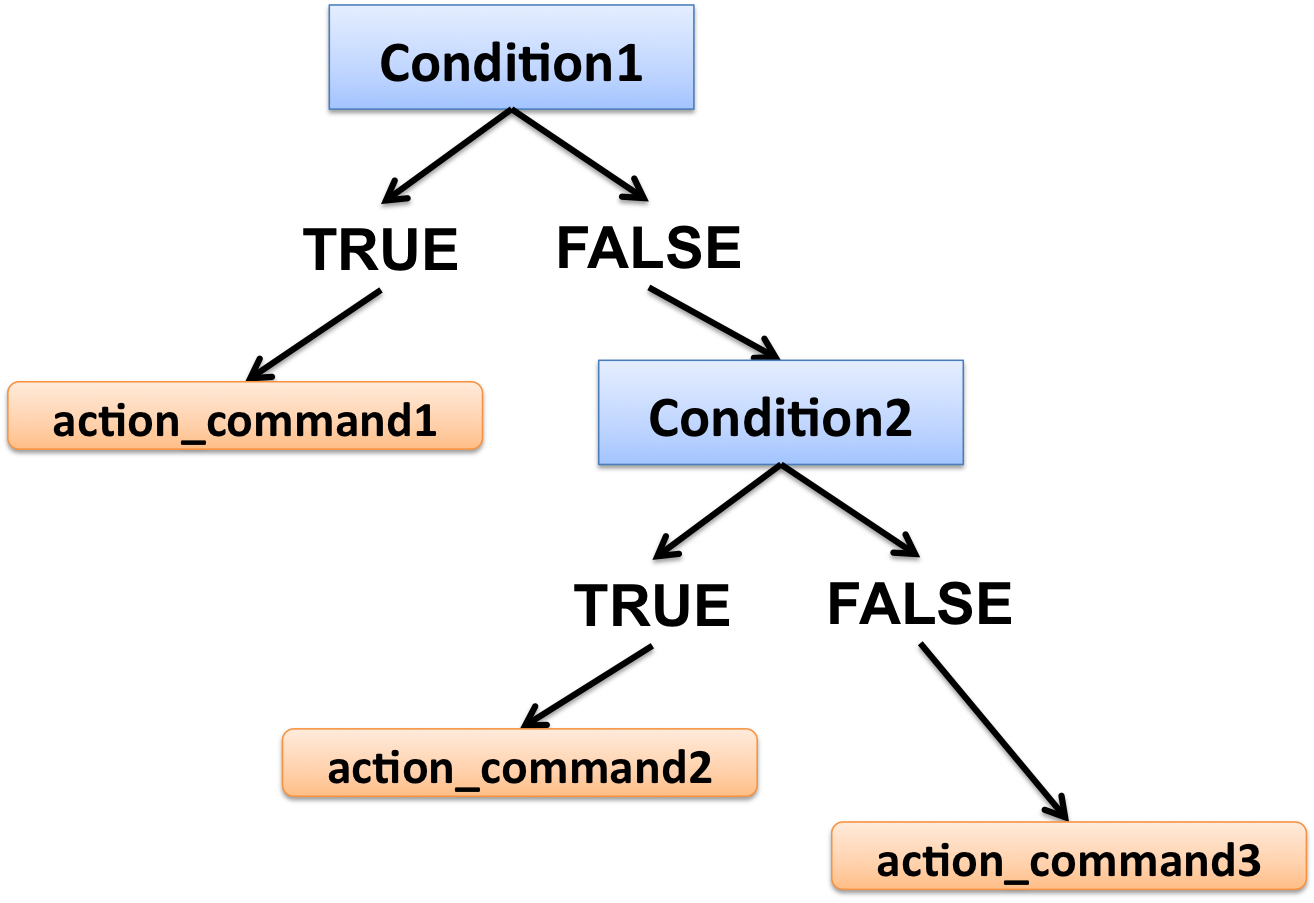
If the condition1 is TRUE, then proceed to the action_command1; if the condition1 is FALSE, test for condition2: if the condition2 is TRUE, proceed to the action_command2; if neither condition1 nor condition2 are TRUE, then proceed to the action_command3 (else).
Note that you can add up as many else if statements as you want, but only one else (not compulsory either).
- Example without else
k <- -2
# Test whether k is positive or negative or equal to 0
if(k < 0){
print("negative")
}else if(k > 0){
print("positive")
}else if(k == 0){
print("is 0")
}- Example with else