9.1 Vectors
A vector is a sequence of data elements from the same type.
| 329 | 45 | 12 | 28 |
9.1.1 Creating a vector
- Values are assigned to a vector using the c command (combining elements).
You can create an empty vector with:
- Create a sequence of consecutive numbers:
vecnum <- 10:16
# same as:
vecnum <- c(10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16)
# both ends (10 and 16) are included- Character vectors: Each element is entered between (single or double) quotes.
| mRNA | miRNA | snoRNA | lncRNA |
9.1.2 Vector manipulation
- A vector can be named: each element of the vector can be assigned a name (number or character)
names(vector1) <- c("mRNA", "miRNA", "snoRNA", "lncRNA")
# use an object which already contains a vector
names(vector1) <- mynames- Get the length (number of elements) of a vector
## [1] 4- Extracting elements from vector a
- extract elements using their position (index) in the vector:
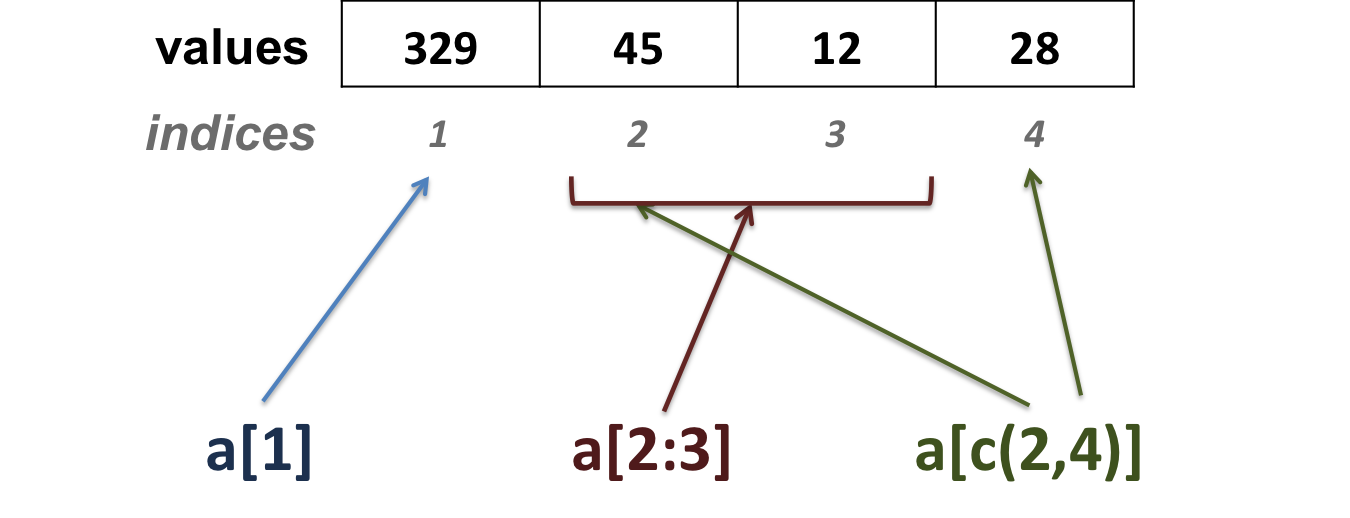
## [1] 10## [1] 10 12## [1] 11 12 13- extract elements using their names:

## mRNA ## 329## miRNA lncRNA ## 45 28 - extract elements using their position (index) in the vector:
- Reassigning a vector’s element
- Removing a vector’s element
- Show versus change
x[-2] ![]() x unchanged !
x unchanged !
x <- x[-2] ![]() x reassigned !
x reassigned !
9.1.3 Combining vectors
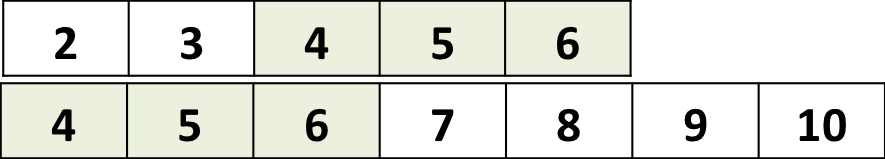
- From 2 vectors a and b you can create a vector d
The elements of v2 are added after the elements of v1
- Likewise, you can add elements at the end of a vector
9.1.4 Numeric vector manipulation
Logical operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| < | less than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| > | greater than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| == | exactly equal to |
| != | not equal to |
| !x | not x |
| x | y | x OR y |
| x & y | x AND y |
- Which elements of a are equal to 2?
## [1] FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
- Which elements of a are superior to 2?
## [1] FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE
- Extract elements of a vector that comply with a condition:
## [1] FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE## [1] 2 3 4 5
9.1.4.1 Operations on vectors
- Adding 2 to a vector adds 2 to each element of the vector:
## [1] 3 4 5 6 7
Same goes for subtractions, multiplications and divisions…
- Multiplying a vector by another vector of equal length
## [1] 4 12 0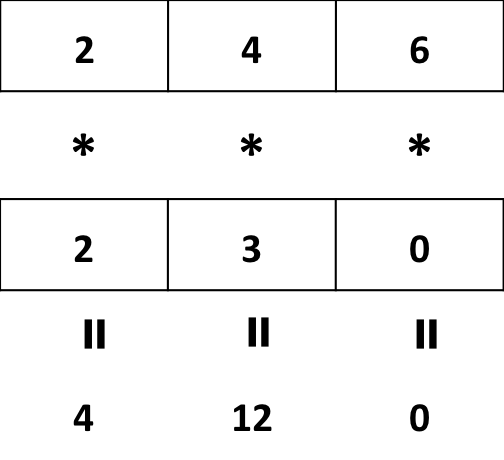
- Multiplying a vector by another shorter vector
## Warning in a * b: longer object length is not a multiple of shorter object
## length## [1] 4 12 0 6 3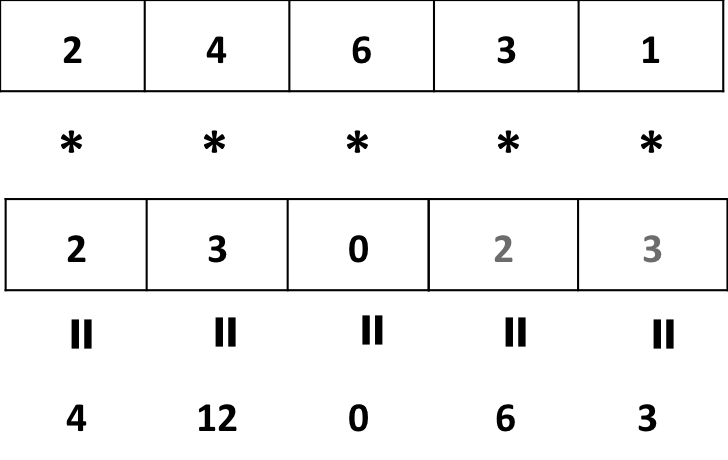
Vector a is “recycled” !
- Summary statistics
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| mean(x) | mean / average |
| median(x) | median |
| min(x) | minimum |
| max(x) | maximum |
| var(x) | variance |
| summary(x) | mean, median, min, max, quartiles |
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 1.00 2.25 3.00 11.00 9.75 45.009.1.5 Character vector manipulation
Character vectors are manipulated similarly to numeric ones.
- The %in% operator:
k <- c("mRNA", "miRNA", "snoRNA", "RNA", "lincRNA")
p <- c("mRNA","lincRNA", "tRNA", "miRNA")
k %in% p## [1] TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE## [1] "mRNA" "miRNA" "lincRNA"- Select elements from vector m that are not exon
## [1] FALSE TRUE FALSE## [1] "intron"